JanusVLN:
Decoupling Semantics and Spatiality with Dual Implicit Memory for Vision-Language Navigation
Abstract
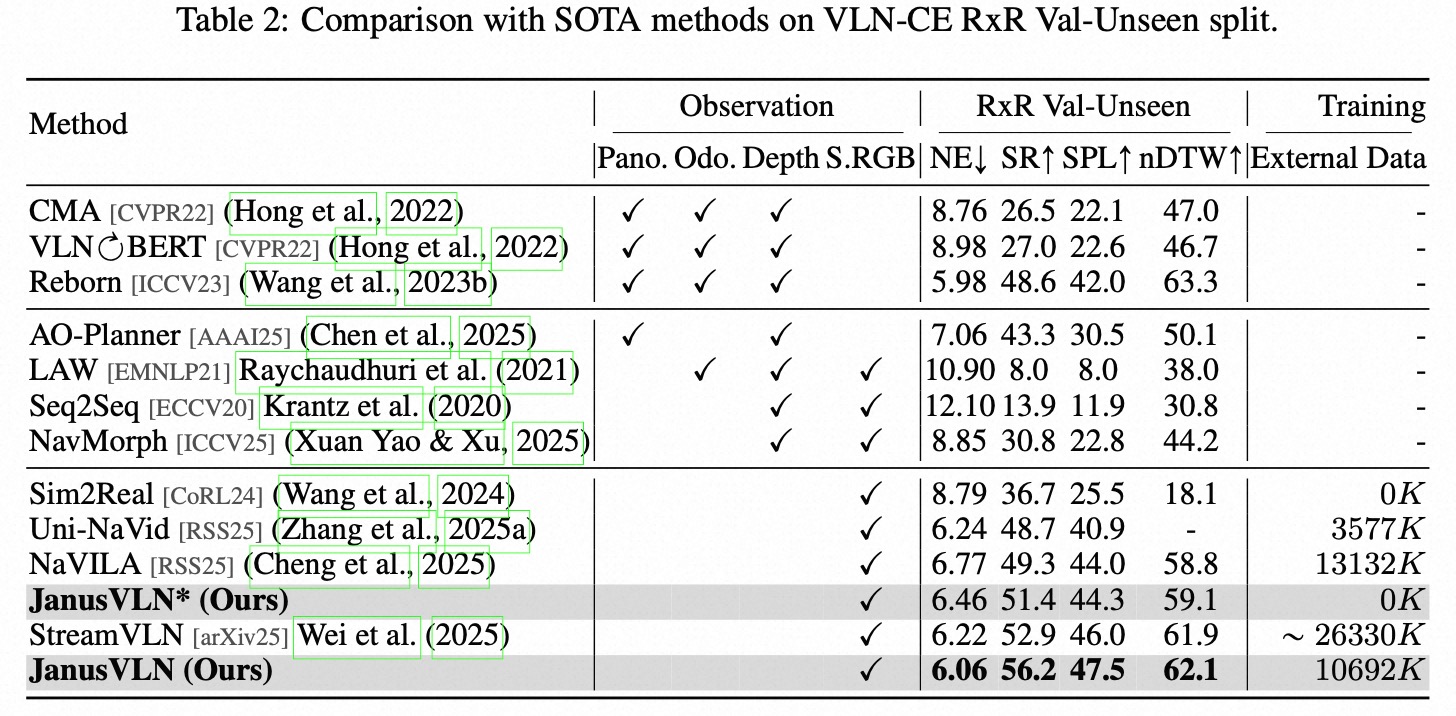
Vision-and-Language Navigation (VLN) requires an embodied agent to navigate through unseen environments, guided by natural language instructions and a continuous video stream. Recent advances in VLN have been driven by the powerful semantic understanding of Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs). However, these methods typically rely on explicit semantic memory, such as building textual cognitive maps or storing historical visual frames. This type of method suffers from spatial information loss, computational redundancy, and memory bloat, which impede efficient navigation. Inspired by the implicit scene representation in human navigation, analogous to the left brain's semantic understanding and the right brain's spatial cognition, we propose JanusVLN, a novel VLN framework featuring a dual implicit neural memory that models spatial-geometric and visual-semantic memory as separate, compact, and fixed-size neural representations. This framework first extends the MLLM to incorporate 3D prior knowledge from the spatial-geometric encoder, thereby enhancing the spatial reasoning capabilities of models based solely on RGB input. Then, the historical key-value (KV) caches from the spatial-geometric and visual-semantic encoders are constructed into a dual implicit memory. By retaining only the KVs of tokens in the initial and sliding window, redundant computation is avoided, enabling efficient incremental updates. Extensive experiments demonstrate that JanusVLN outperforms over 20 recent methods to achieve SOTA performance. For example, the success rate improves by 10.5-35.5 compared to methods using multiple data types as input and by 3.6-10.8 compared to methods using more RGB training data. This indicates that the proposed dual implicit neural memory, as a novel paradigm, explores promising new directions for future VLN research.
Demo Video
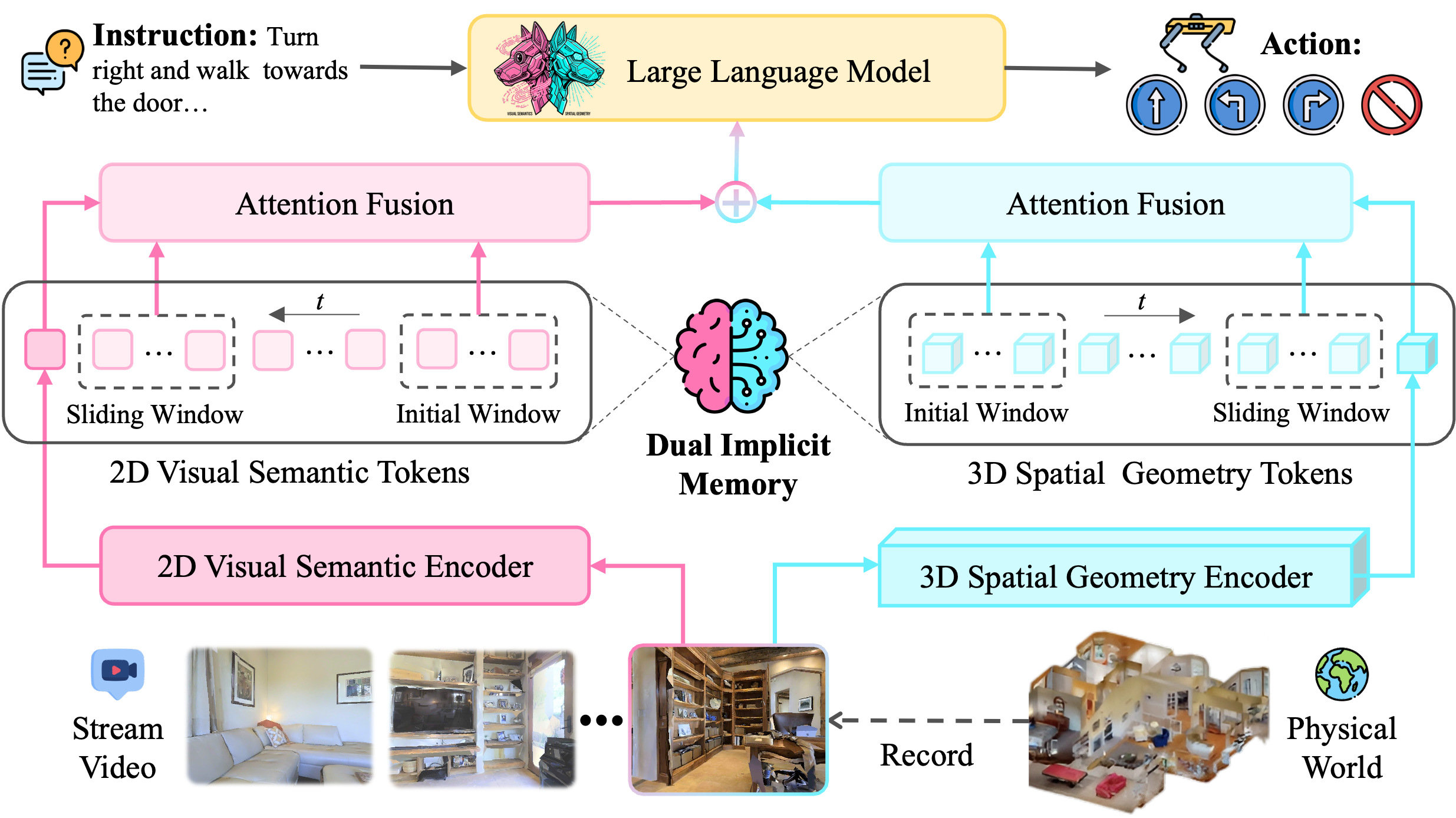
Approach
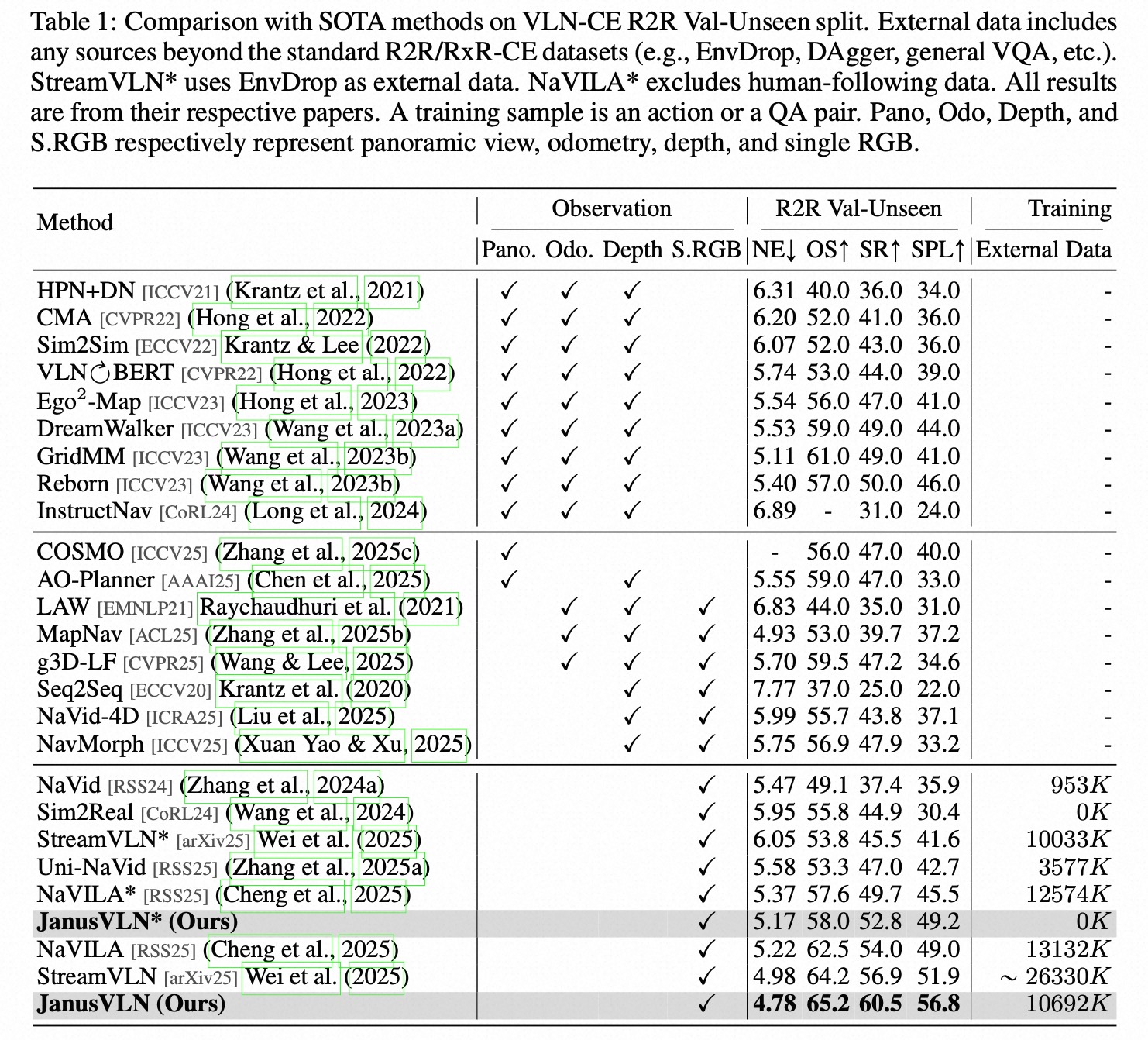
Experiment
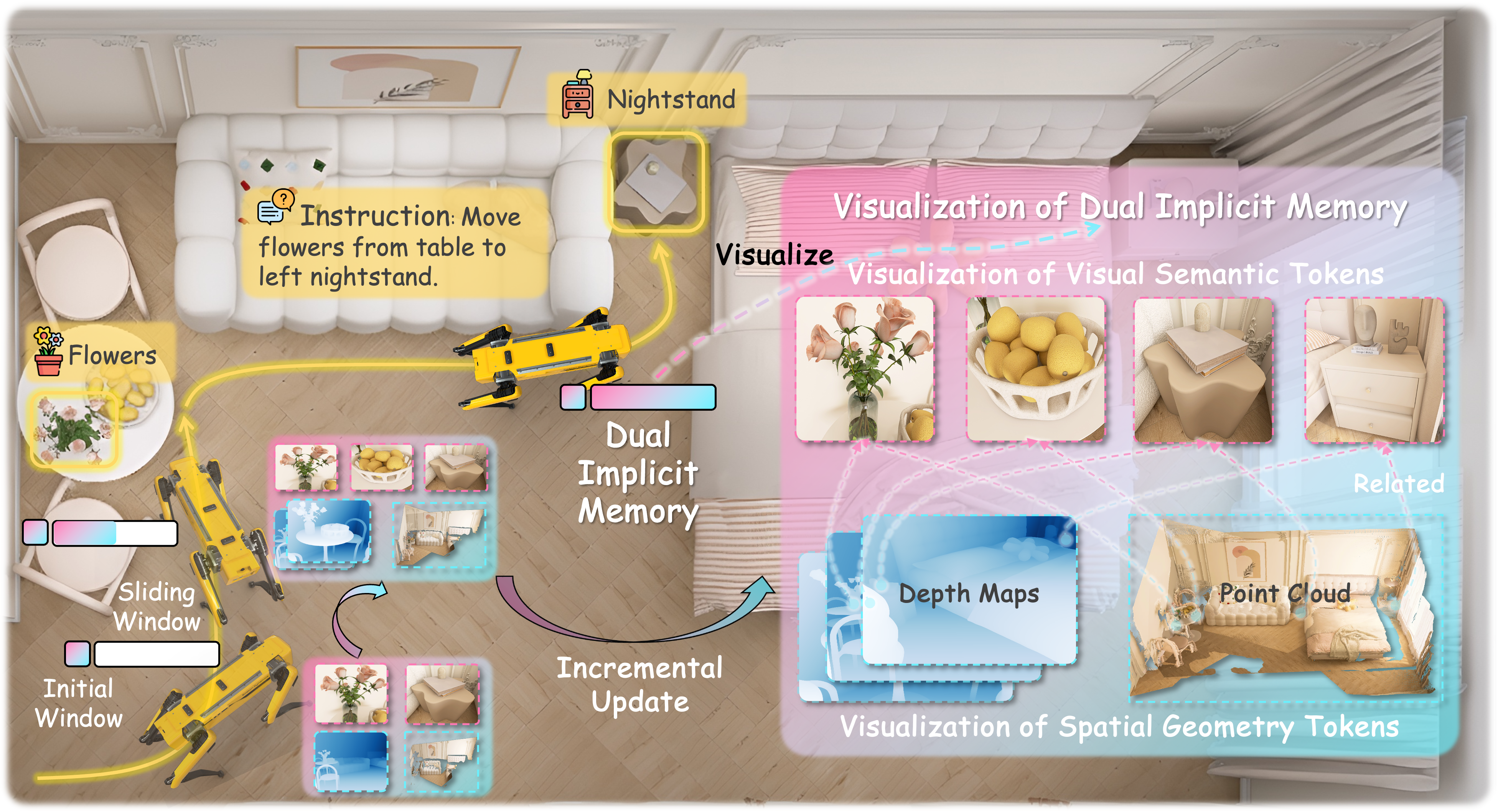
Real-World Visualization
VLN-CE Visualization
BibTeX Citation
@article{zeng2025janusvlndecouplingsemanticsspatiality,
title={JanusVLN: Decoupling Semantics and Spatiality with Dual Implicit Memory for Vision-Language Navigation},
author={Shuang Zeng and Dekang Qi and Xinyuan Chang and Feng Xiong and Shichao Xie and Xiaolong Wu and Shiyi Liang and Mu Xu and Xing Wei},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2509.22548},
year={2025}
}

